An ultra-sensitive ratiometric fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid detection by the synergistic effect of AIE and TBET and its application of detecting exogenous/endogenous HOCl in living cells
 © Royal Society of Chemistry 2019
© Royal Society of Chemistry 2019Abstract
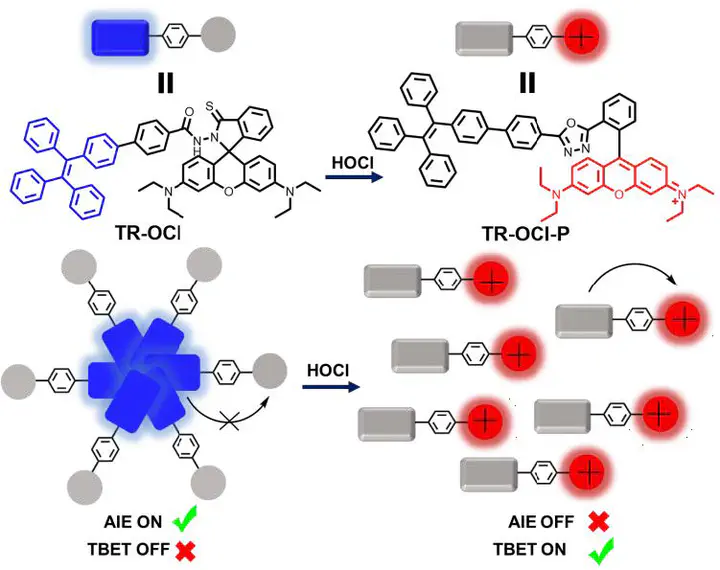
An ultra-sensitive and ratiometric fluorescent probe for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) detection based on the mechanism of aggregation induced emission (AIE) and through-bond energy transfer (TBET) has been reported herein. By exploiting the advantages of AIE and TBET, which eliminates emission leakage from dark donors, the probe exhibits ultra-high sensitivity towards HOCl by an enhancement of over 7000-fold in the fluorescence ratio (I589 nm/I477 nm), which is one of the highest recorded so far. The reaction mechanism has been discussed in detail, and the effects of interferents and the reaction kinetics have also been investigated. Lastly, the successful result of exogenous/endogenous HOCl imaging detection in different cell lines indicates the potential use of the probe in living systems.